
Why The OpenAI GPT-5.1 Announcement Matters?
OpenAI GPT-5.1 announcement, 12 November 2025, matters because it upgrades reasoning and agentic workflows. The latest GPT-5.1 is “a smarter, more conversational ChatGPT,” according to the official blog. OpenAI GPT-5.1 highlights adaptive reasoning that runs two to three times faster than GPT-5 on complex tasks.
GPT-5.1 reinforces three roadmap themes for product teams:
- 1Adaptive reasoning for variable-depth thinking in real workloads.
- 2Long-horizon agents that sustain multi-hour coding and refactoring sessions.
- 3Developer efficiency through cheaper prompt caching and stronger coding tools.
How The OpenAI GPT-5.1 Launch Changes Product And Engineering Decisions
The OpenAI GPT-5.1 launch changes product and engineering priorities by shifting roadmaps toward deeper reasoning, longer tasks, and stricter cost control. Product leaders now evaluate OpenAI GPT-5.1 release news in terms of attach-rate, cross-sell, and how quickly new features can rely on more reliable agents instead of simple chat flows.
Source: OpenAI
For many teams, “GPT 5.1 vs GPT 5” differences became the default planning questions, especially given benchmarks showing higher success rates on multi-step tasks and faster median latency.
- Product leaders focus on roadmap bets, pricing tiers, and user outcomes.
- Engineering focuses on latency budgets, reliability SLOs, migration effort, tooling, and guardrails.
Overview Of GPT-5 Models Before The GPT-5.1 Release
GPT-5 serves as the foundation for GPT-5.1, which upgraded reasoning depth and speed without changing core interfaces.
Typical GPT-5 usage includes:
- Production chat and copilots that need stable reasoning.
- Code generation, refactoring, and agentic tool use.
- High-token RAG, planning, and batch analysis workloads.
For product leaders, the GPT 5.1 vs 5 question reduces to this: GPT-5.1 keeps GPT-5’s breadth while improving reliability, reasoning depth, and cost behaviour for real products.
Business outcomes teams typically see when upgrading to GPT-5.1:
- Higher task resolution rates on complex journeys, often 5–10 percentage points.
- Fewer manual reviews because instructions stick more reliably across long sessions.
- Reduced retries and fallbacks, which lowers effective cost per successful task.
- More confident rollout of agentic workflows, since gpt-5 vs gpt-5.1 differences favour sustained reasoning over many steps.
GPT-5.1 Improvements In Reasoning, Reliability, And Latency
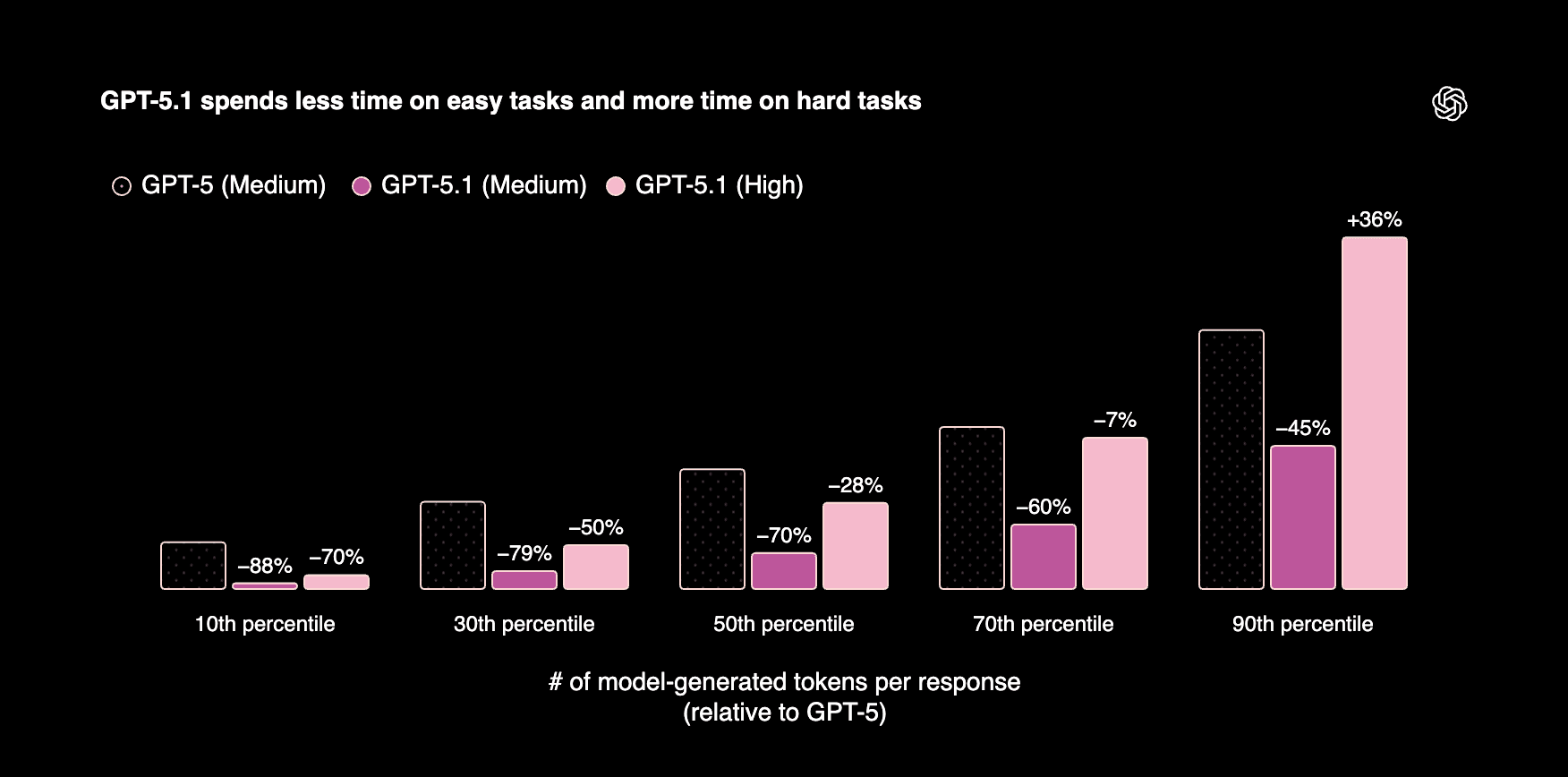
GPT-5.1 highlights three headline: stronger reasoning, higher reliability, and significantly lower latency. Together, these changes make the model more suitable for long-horizon coding agents, complex support flows, and research workflows that previously felt too slow or fragile.
Recent GPT 5.1 benchmarks show that these gains are not just marketing but measurable shifts in real tasks. Product and engineering teams can treat them as levers for resolution rate, error budgets, and end-user responsiveness.
- Reasoning: OpenAI and independent reports show that GPT-5.1 reaches about 76.3% on SWE-bench Verified, versus roughly 72.8% for GPT-5, improving the success rate for difficult bug fixes in agentic codebases.
- Latency: The same launch materials show simple coding prompts dropping from roughly 10 seconds to about 2 seconds, and Sierra measures a 20% improvement in low-latency tool-calling, which compounds across coding IDEs, support triage bots, and research assistants.
GPT-5.1 New Features For Agents, RAG, And Workflow Automation
GPT-5.1's new features focus on making agents more capable, RAG more dependable, and workflow automation easier to orchestrate at scale. OpenAI describes GPT 5.1's new features like improved tool use, better long-context behavior, and more stable function calling across complex tasks, tuned for production agents rather than only chat use.
- Agents and tool use: GPT-5.1 strengthens multi-step tool-calling and planning for long-horizon agents, with OpenAI reporting higher success rates than GPT-5 on dynamic multi-tool evaluations. In one 2025 case study, an insurance workflow agent completed end-to-end claim triage with roughly 10–15 percent fewer human escalations than before.
- Retrieval and RAG: For retrieval-heavy workloads, GPT-5.1's new features include more robust instruction following over large contexts and better grounding across multi-document prompts. External benchmarks note improved factual accuracy on long-context QA compared to GPT-5, which reduces hallucination risk in RAG-backed assistants.
- Workflow automation and orchestration: The OpenAI GPT-5.1 instant thinking release combines fast “Instant” responses with deeper “Thinking” passes for complex calls, so orchestrators can balance speed and depth. OpenAI highlights up to 2–3 times faster responses on typical coding and support actions, directly improving automated workflow throughput.
GPT-5.1 Codex And Coding-Focused Enhancements For Engineering Teams
GPT 5.1 codex refers to GPT-5.1’s coding-specialised capability, tuned for long-horizon edits, multi-file reasoning, and agentic development workflows. Within the GPT-5.1 OpenAI family, Codex and Codex-max target IDE integrations, CI pipelines, and autonomous coding agents that must maintain consistency across many files over time. Early 2025 evaluations report higher pass@k on competitive coding benchmarks compared with GPT-5-era models, especially for multi-step bug fixing and refactors.

Source: OpenAI
These models help engineering teams manage long-horizon refactors, coordinated multi-file edits, and systematic test generation while keeping context about previous changes. In several public case studies, GPT-5.1 OpenAI release materials highlight agents that keep repositories in a healthy state, automatically updating tests and configs after each change. This shift matters most in large monorepos, where manual review alone struggles to keep pace with frequent deploys.
Representative scenarios for GPT 5.1 Codex and Codex-max include:
- Framework upgrade across dozens of services, with automatic API surface adjustments
- Migration of services between runtimes or clouds, including config and IaC updates
- Automated PR suggestions that propose fixes, tests, and documentation in one shot
- Large test-suite generation to raise coverage for legacy modules with minimal engineer time
The GPT-5.1 Model Lineup And OpenAI API Options
GPT-5.1 is positioned as the flagship in the OpenAI API models. The models are optimised for high-stakes reasoning and long-horizon agents. OpenAI’s Docs describe the GPT 5.1 API as the default choice for complex coding, advanced assistants, and multi-step workflows, while GPT-5 and GPT-5 mini cover broader and lighter use cases.
Use guidelines within the openai gpt-5.1 api release context:
- Use GPT-5.1 api for agentic workflows, complex coding, and premium user tiers.
- Use GPT-5 for balanced cost-quality assistants and RAG-backed chat.
- Use GPT-5 mini for simple routing flows, FAQs, and very high-volume endpoints.
GPT-5.1 Release Tiers: General, Mini, And Specialized Models
OpenAI release spans three tiers: a general GPT-5.1 model, lighter GPT-5 mini variants, and specialised GPT-5.1 Codex models for code-heavy workloads. OpenAI’s own model and pricing docs present GPT-5.1 as the flagship for coding and agentic tasks, with GPT-5 mini as a faster, cheaper option for well-defined flows.
These figures align with the OpenAI pricing page models GPT-5, which lists GPT-5.1 and GPT-5 mini at $1.25 and $0.25 per million input tokens, respectively, with $10 and $2 per million output tokens.
The OpenAI pricing models GPT-5 layout helps teams choose quickly:
- Scan tiers for capability-to-budget across GPT-5.1, mini, and nano.
- Match workload class (agentic, chat, batch) to each row on the page.
- Estimate total cost by combining token prices with expected traffic volume.
How To Choose Between GPT-5 And GPT-5.1 In The OpenAI API Models GPT-5 Family
Choosing between GPT-5 and GPT-5.1 is simple: GPT-5 is usually enough for straightforward assistants and tools,. Use this checklist when evaluating GPT-5.1 OpenAI against GPT-5:
- Quality and reasoning needs: Choose GPT-5.1 if agents frequently plan, call tools, or debug; GPT-5.1 running 2–3x faster than GPT-5 while outperforming it on dynamic evals.
- Latency budget: Prefer GPT-5.1 for latency-sensitive UX, since OpenAI’s docs show faster responses on simple tasks at similar quality.
- Cost constraints: Pricing for both models is identical at $1.25 per million input tokens and $10 per million output tokens, so cost differences mostly come from fewer retries and better caching with GPT-5.1.
- Dependency on gpt-5.1 new features: Adopt GPT-5.1 when extended prompt caching,
reasoning_effort="none", or tools likeapply_patchare required for your workflows.
Before large migrations, teams should A/B test across openai api models GPT-5, routing a slice of production traffic to GPT-5.1 and measuring resolution rate, latency, and cost per successful task.
Pricing, Cost Planning, And The OpenAI Pricing Page Models GPT-5
The OpenAI pricing page models GPT-5 explains exactly how GPT-5 and GPT-5.1 bill input, cached input, and output tokens. GPT-5.1 lists input at $1.25 per million tokens, cached input at $0.125, and output at $10 per million, giving a 90 percent discount on repeated cached tokens. OpenAI describes GPT-5.1 as “the best model for coding and agentic tasks,” which signals that the GPT-5.1 release openai pricing is tuned for heavy workflow usage.
Consider a concrete example. A request that uses 5,000 input tokens and 1,000 output tokens on GPT-5.1 costs about $0.016, combining $0.00625 for input and $0.01 for output using the posted rates. That structure on the OpenAI pricing models GPT-5 page lets teams estimate cost per user action rather than only per token.
Key cost behaviours on the OpenAI pricing page models GPT-5:
- When caching helps: High-repeat prompts or shared context chunks benefit most from the 90 percent cached-input discount.
- Impact of long context: Very long prompts dominate cost; batching and truncation strategies matter more than model choice.
- GPT-5 vs GPT-5.1: Unit prices are identical, so effective savings come from fewer retries and smarter reasoning settings in GPT-5.1, not list-price differences.
Cost-Control Patterns With GPT-5.1 API
Cost control becomes crucial after the OpenAI GPT-5.1 launch because higher-capability agents can silently inflate spend through longer contexts and more calls per workflow. The GPT 5.1 api keeps list prices aligned with GPT-5, so savings now depend on architecture choices rather than cheaper tokens alone, a point OpenAI stresses in the OpenAI GPT-5.1 rollout announcement and pricing docs.
Key patterns for controlling cost while still benefiting from GPT-5.1 improvements:
- Aggressive caching for repeated prompts: Cache system prompts, RAG headers, and shared instructions; raising the cache hit rate from 30% to 70% can cut effective input cost by roughly 50%.
- Routing light tasks to smaller GPT-5 models: Send FAQ, routing, and simple checks to GPT-5 mini or nano.
- Tuning reasoning effort: Use minimal reasoning for easy calls and higher effort only on complex steps.
- Truncating or compressing context: Strip unused history and summarise long threads before each GPT 5.1 api call.
Together, these patterns, combined with OpenAI’s caching discounts and tiered model lineup, keep per-outcome costs predictable while still exploiting GPT-5.1's improvements in reasoning and reliability.