Picture this: You’re staring at dozens of files that need updates. Your deadline is tomorrow. But what if you had a smart assistant? One that understands your entire codebase and can change multiple files at once?
That’s precisely what code editing composers do.
These AI tools live inside your code editor. They help you write and change code faster than ever. They understand both plain English and programming languages. Tell them what you want to build or fix, and they work across your project.
Cursor AI leads this revolution. Their Composer feature, released in late 2024, changed how developers work. It lets them create entire applications from simple descriptions. Developers now focus on the big picture while AI handles the details.
The impact? It’s massive:
- 1Tasks that took hours now take minutes
- 2Developers build prototypes faster than ever
- 3Bug fixes can spread across multiple files instantly
- 4Entire sections of applications appear from just a few prompts
This isn’t about replacing programmers. It’s about giving them smarter tools. These composers transform coding from line-by-line writing to orchestrating how code comes together. They make coding more accessible and development more efficient.
The result? Both experts and newcomers can build better software faster than ever before.
1. Understanding the Cursor composer
First, let’s understand the Cursor Composer – what is it, and how does it work?
1.1 What is Composer in Cursor.ai
Cursor Composer is an AI-powered feature that generates and modifies multiple files of code based on natural language instructions or prompts. It acts as a command center where developers can describe what they want to build, and the AI creates entire applications. This could also include proper file structures, dependencies, and working code.
Unlike basic code completion tools, Composer understands project-wide context and can make coordinated changes across multiple files while maintaining consistent coding standards.
It is like having a smart coding partner right inside your computer. Think of it as a translator between your ideas and actual code. You have the idea and the Composer has the skills and logical reasoning capabilities to build your idea.
Here’s how it works:
- 1You type what you want to build in plain English
- 2The Composer understands your request
- 3It creates all the necessary code across multiple files
- 4You can review and adjust what it makes
Source: Andrej Karpahty on X
Let’s look at a real example. Say you tell the composer: "Create a simple web server." It will:
- Set up the basic file structure
- Add required code libraries
- Write the main server code
- Create configuration files
- Add helpful comments explaining the code
Check out this video and see how cursor.ai sets up a full working file structure for Unity.
The magic happens in how it handles everything at once. You don’t need to jump between files or remember complex setup steps. The Composer does this heavy lifting for you.
Modern composers like Cursor AI go even further. They can:
- Read your entire project
- Suggest improvements
- Fix errors across multiple files
- Generate new features based on your existing code
The best part? You stay in control. The Composer suggests and creates, but you decide what to keep, change, or remove.
1.2 Use cases; vibe coding
People have been using Cursor.ai a lot. A term that was invented by Andrej Karpathy is “vibe coding.”
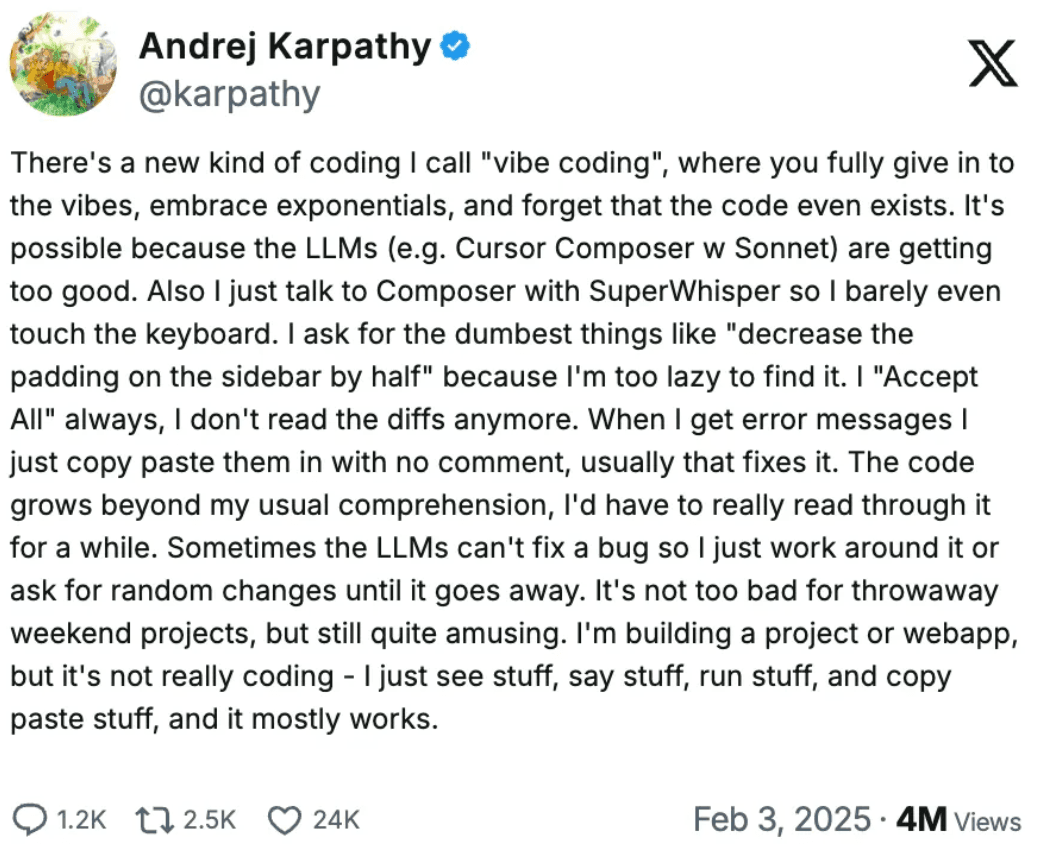
Source: Andrej Karpahty on X
It is essentially you explaining the ideas to cursor.ai with some language model, and it does coding for you. And many in the developer community have started using voice commands to code.
Here are some use cases that I found interesting.
- Cursor AI supports image input. If you are a UI designer, you can feed the input to Cursor AI, and it will generate relevant code for you.

Source: Features | Cursor
- You can ask cursor.ai to access web and find the latest updates, syntax, library, etc for you.
So, essentially it is like a chatbot like ChatGPT or Perplexity that can search the internet and solve code-related issues? Yes, but partially. It is more than that.
Let’s understand the difference between a chat and a composer.
2. What is the difference between a chat and a composer?
I’ve been exploring both Cursor’s Chat and Composer features lately. Let me share what I’ve learned about their differences and overlap.
The Core Difference:
- Chat is like having a coding tutor - it explains and guides
- Composer acts as a coding partner - it builds and changes things
Let’s talk about how they work. Chat has been around longer. It's great for understanding code and making single-file changes. You ask questions, it explains problems, and you can accept its suggestions when ready.
Composer is the newer tool. It feels different because:
- It can edit multiple files at once
- Changes happen in real-time
- The interface can float or go full-screen
- It saves changes automatically
Here’s what's interesting: there’s definitely some overlap. Both can write code and make changes. But Composer seems more powerful. It does everything Chat does, plus handles entire projects at once.
Why have both? Good question.
The dual interfaces might seem confusing at first. Chat still feels more natural for quick questions and learning. Composer shines when you’re building features or making big changes.
My take? Chat works best when you’re:
- Debugging issues
- Learning new concepts
- Making small changes
Use Composer when you need to:
- Build new features
- Update multiple files
- Generate entire applications
For now, both tools serve their purpose. Whether they’ll merge in the future? That’s something only the Cursor team knows. But for developers, having both options gives us flexibility in how we work.
Remember: The tools might overlap, but they each have their sweet spot. Use what works best for your current task.
Below, I have provided a detailed comparison of chat and composer.
These are the features of the composer. But what makes the Composer work or execute tasks in such a manner? For that, we need to understand what the Composer is made of and what are components of the Composer are.
3. Components of the composer
The Composer has six major components. These allow the Composer to work seamlessly, adhering to the user’s request.
1. AI model integration
- Processing: Turns your natural language into actionable coding tasks
- Generation: Creates code that matches your project's style and standards
- Learning: Adapts to your codebase patterns and preferences over time
- Consistency: Ensures all generated code follows the same conventions
2. Code understanding system
- Scanner: Maps your entire project like a detailed city blueprint
- Analyzer: Finds connections between different parts of your code
- Pattern recognition: Learns how your existing code is structured
- Dependency mapping: Tracks how different files rely on each other
3. File management
- Reader: Opens and understands existing code files intelligently
- Creator: Builds new files with proper naming and locations
- Updater: Changes multiple files while maintaining their relationships
- Organizer: Keeps your project structure clean and logical
4. User interface
- Command center: Takes your instructions in plain English
- Preview zone: Shows you changes before they happen
- Navigation: Helps you move through affected files easily
- Flexibility: Adapts between floating and full-screen modes
5. Change comparison system
- Additions: Highlights new code in green for easy spotting
- Deletions: Shows removed code in red for clear tracking
- Modifications: Points out changed sections with clear markers
- Overview: Gives you a complete picture of all changes at once
6. Change application system
- Executor: Applies your approved changes safely
- Formatter: Keeps your code looking clean and consistent
- Multi-file handler: Updates several files in the right order
- Dependency tracker: Makes sure all connected parts stay working
Now, let’s try to build our composer.
4. Building your own composer: Step-by-step guide
In this section, I will explain how you can make your Composer using Python and OpenAI API.
4.1. Choosing the LLM
For this tutorial, I will be using GPT4 as it is versatile and has good reviews over any OpenAI model.
Why GPT-4?
OpenAI GPT-4 has emerged as a leading choice for code editing applications for several reasons:
- 1Contextual understanding: GPT-4's ability to understand and maintain context across large codebases makes it ideal for complex projects.
- 2Multi-language proficiency: It demonstrates exceptional performance across numerous programming languages and frameworks.
- 3Code quality: The model consistently produces clean, well-documented code that follows best practices.
- 4API maturity: OpenAI's API infrastructure is battle-tested and reliable, with comprehensive documentation.
But you can still use Anthropic models or any open-source models (preferably from Huggingface).
4.2. Setting the environment
We will use conda to set up the environment and name it “code_composer.”
4.3. Install the required packages
Let’s install all the necessary packages for this simple project.
Explanation:
- os: For file system operations (reading/writing files).
- difflib: To compare original and generated code.
- openai: To interact with OpenAI’s API.
You can learn more about setting up your API key from here.
4.4. Integrating with file system
We will be using Python’s os and pathlib for file operations. File system integration forms the backbone of our composer, handling reading and writing operations with proper error management.
Explanation
- read_file: Opens a file in read mode ('r') with UTF-8 encoding for broad compatibility. Includes error handling for missing files or read issues.
- write_file: Overwrites the file with new content in write mode ('w'). Also handles potential errors gracefully.
4.5. Provide codebase context
The context-gathering system helps the AI understand your project by collecting and formatting code from multiple files in a way the model can process effectively.
Explanation:
- Takes a list of file paths (e.g., from user input).
- Checks if each file exists using os.path.exists.
- Formats the context with file paths as headers (e.g., # path/to/file.py) for clarity in the AI prompt.
- Skips missing files with a warning to keep the process robust.
4.6. Create a UI
A simple command-line interface accepts user instructions and file paths, making it easy to interact with the Composer without complex UI elements.
Explanation:
- Prompts the user for an instruction (e.g., “Create a login function”).
- Asks for file paths in a comma-separated format (e.g., main.py, utils.py).
- Processes the input into a clean list for use in get_context.
4.7. Process the instruction with AI model
The AI processing core takes user instructions and project context, sending them to GPT-4 through OpenAI's API to generate appropriate code changes.
Explanation:
- Prompt: Combines context and instruction with a directive to return only code (no chatter).
- Parameters:
- Error Handling: Returns an empty string if the API call fails, keeping the program running.
4.8. Present code changes with a diff viewer
We’ll use difflib to show differences between the original and AI-generated code, helping the user review changes.
Explanation:
- difflib.unified_diff: Creates a standard diff format (e.g., - for removed, + for added lines).
- Labels the diff with file paths for clarity.
- Prints each line of the diff, making it easy to review.
4.9. Apply changes
A straightforward approval system lets developers review and accept or reject the AI's proposed changes before they're applied to the codebase.
Explanation:
- Prompts the user with a simple y/n choice.
- Calls write_file if approved; otherwise, skip.
- Returns a boolean to track whether changes were applied.
4.10. Tie it all together
The main function streamlines all components into a smooth workflow, from getting user input to applying final changes.
Explanation:
- Orchestrates the workflow: input → context → generation → review → apply.
- Handles one file at a time for simplicity. The AI should output changes per file in a real tool, parsed accordingly.
- Includes basic error checking (e.g., no context, no generated code).
Conclusion
Code editing composers like Cursor AI represent a significant leap in developer productivity, enabling faster prototyping and more efficient code management. This article provided a deep dive into how composers work, their key components, and even a practical guide to building one using Python and the OpenAI API.
Key learnings:
- Composers differ from chat interfaces by handling multi-file operations and project-wide changes
- Six core components power composers: AI Model, Code Understanding, File Management, UI, Change Comparison, and Change Application
- Building a basic composer requires understanding file system integration, context gathering, and AI model processing
How different roles can leverage composers:
Product Managers:
- Use composers to prototype features and validate ideas rapidly
- Reduce development time by automating boilerplate code generation
- Better understanding technical implications through AI-guided code reviews
AI Engineers:
- Build custom composers tailored to specific development workflows
- Integrate multiple AI models for specialized code generation tasks
- Implement safeguards and validation systems for AI-generated code
Startup Leadership:
- Accelerate MVP development and iteration cycles
- Reduce technical debt through consistent code generation
- Lower onboarding time for new developers joining the project
- Save development costs by automating routine coding tasks
The future of development lies in tools that augment human creativity with AI efficiency. Composers like Cursor AI are just the beginning of this transformation in software development.